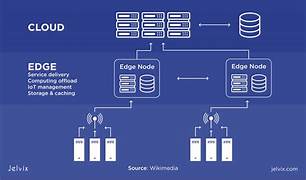
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network, closer to where data is generated or used. This can improve performance, reduce latency, and increase security.
Edge computing is a natural evolution of cloud computing. Cloud computing has been very successful in providing scalable and cost-effective computing resources. However, cloud computing has some limitations. One limitation is that it can be slow to process data that is generated at the edge of the network. This is because the data has to travel a long distance to reach the cloud. Another limitation is that cloud computing can be vulnerable to security threats. This is because data has to travel over public networks to reach the cloud.
Edge computing addresses these limitations by bringing computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network. This can improve performance by reducing the distance that data has to travel. It can also increase security by reducing the amount of time that data is exposed to public networks.
There are a number of different ways to implement edge computing. One way is to use fog computing. Fog computing is a type of edge computing that uses a distributed network of small, lightweight devices to process data. These devices are typically located at the edge of the network, close to where data is generated.
Another way to implement edge computing is to use micro data centers. Micro data centers are small, modular data centers that can be deployed at the edge of the network. These data centers are typically more powerful than fog devices, but they also require more power and cooling.
Edge computing is a promising new technology that has the potential to improve performance, reduce latency, and increase security for a wide range of applications. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, edge computing will become increasingly important.
Here are some of the benefits of edge computing:
- Improved performance: Edge computing can improve performance by reducing the distance that data has to travel. This is especially important for applications where real-time response is critical, such as self-driving cars and industrial automation.
- Reduced latency: Edge computing can reduce latency by processing data closer to where it is generated. This can improve the user experience for applications such as video streaming and online gaming.
- Increased security: Edge computing can increase security by reducing the amount of time that data is exposed to public networks. This can help to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Here are some of the challenges of edge computing:
- Cost: Edge computing can be more expensive than cloud computing, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Complexity: Edge computing can be more complex to manage than cloud computing. This is because there are a larger number of devices to manage and the devices are often located in remote locations.
- Security: Edge computing can be more vulnerable to security threats than cloud computing. This is because the devices are often located in remote locations and they are connected to the internet.
Overall, edge computing is a promising new technology that has the potential to improve performance, reduce latency, and increase security for a wide range of applications. However, there are some challenges that need to be addressed before edge computing can become mainstream.
Here are some of the use cases for edge computing:
- Smart cities: Edge computing can be used to power smart city applications such as traffic management, public safety, and energy management.
- Industrial automation: Edge computing can be used to improve the efficiency and productivity of industrial processes.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing can be used to process data from IoT devices in real time.
- Media and entertainment: Edge computing can be used to deliver high-quality video streaming and online gaming.
- Healthcare: Edge computing can be used to collect and analyze medical data in real time.
Edge computing is a rapidly evolving technology with a wide range of potential applications. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, edge computing will become increasingly important.